 A rash of any kind can be annoying, painful, and embarrassing. However, when it comes to a rash behind the ear, it can be a cause for concern.
A rash of any kind can be annoying, painful, and embarrassing. However, when it comes to a rash behind the ear, it can be a cause for concern.
As with most rashes, it can appear red, swollen, and irritated before it becomes a blister or open sore.
Usually stemming from the head or neck region, a rash behind the ears occurs when moisture sets into the folds of the skin.
We will examine five common causes and treatments for this unusual type of rash, and discover when to seek the professional help of a dermatologist.
What Causes a Rash Behind the Ear?
There are many skin disorders that cause a rash behind ear, as well as environmental conditions such as the weather (heat, sun, cold, and wind). Infections in the body region of the head can be a factor, as can genetics and allergies. These are the five main causes of a rash behind the ear.
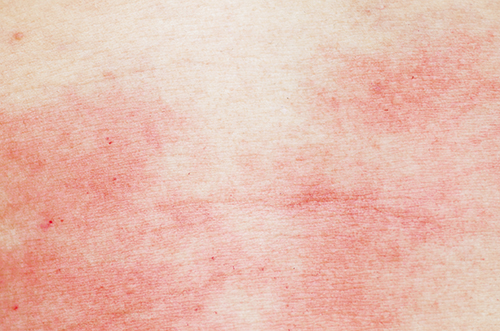
1. Atopic dermatitis, or commonly known as eczema, appears as dry, itchy skin that once inflamed, becomes red and swollen. If not treated, it can become a cluster of blisters. Known to affect mainly young children, this skin rash can also be a problem for adults, typically behind the ears, and in the folds of the elbows and knees. Environmental and genetic factors are usually to blame, and those with allergies or asthma, are at a high risk for atopic dermatitis. It can be painful at times, but is one of the chronic diseases that is very treatable.
2. Contact dermatitis is sometimes confused with atopic dermatitis, as it also appears as a red, swollen, itchy rash on dry, rough skin. The main difference is that contact dermatitis is usually caused by contact with an allergen. People of all ages can develop this type of ear rash, depending on their reaction to substances such a shampoo, soap, cosmetics, jewelry, and cleaning chemicals. Due to the unexpected reactions to substances, it is thought this type of skin condition may be caused by the genetic make-up of a person.
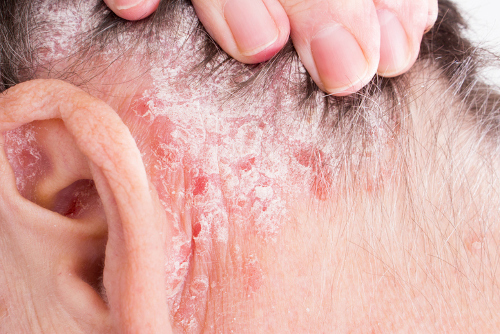
3. Seborrheic dermatitis is another chronic skin condition that first appears on the scalp before spreading to behind ear and on face. A crusty yellowish color, it can be an itchy, greasy, scaly rash. It can also be present in babies as cradle cap and as dandruff in young people and adults. Although the exact cause is not known, it is associated with low-functioning immune systems, a reaction to the skin’s natural occurring yeasts, and an excessive intake of vitamin A. It also has been suggested that a diet lacking in zinc, riboflavin, biotin, and pyridoxine may trigger seborrheic dermatitis.
4. Scalp psoriasis is an extension of the chronic skin condition, psoriasis. While psoriasis is concentrated on the elbows, knees and scalp, scalp psoriasis covers the forehead, neck and behind the ears. Usually, the skin can be shiny and smooth, or appear red and scaly with an itchy surface. However, with atypical psoriasis, neither of these apply. The rash can be reoccurring. Thought to be an autoimmune disease, genetic and environmental factors tend to play a role, but the cause of scalp psoriasis is not known.
 5. Skin infections can cause rash behind the ears, primarily the common tinea capitis and impetigo. Tinea capitis infection, or scalp ringworm, is caused by a type of fungi known as dermatophytes.
5. Skin infections can cause rash behind the ears, primarily the common tinea capitis and impetigo. Tinea capitis infection, or scalp ringworm, is caused by a type of fungi known as dermatophytes.
With its predilection for skin, it can appear anywhere on the body, with main areas being the scalp, feet, and groin regions. It’s a superficial infection that presents as a dry, scaly, red rash that is itchy and forms circles.
Impetigo skin infections are contagious and can be very painful red, swollen blisters that stem from cuts in the skin.
It is usually caused by the bacteria staphylococci, but other bacteria forms may be involved. This superficial infection can lead to serious conditions if not treated.
How to Get Rid of Rash behind the Ears?
Depending on the type and severity of the rash, there may be home remedies and over-the-counter medications that can help with rash behind ear treatment and prevention of it spreading. It’s important to ensure the skin behind ears is always dry and clean to prevent rashes and other skin conditions.
Unfortunately, atopic dermatitis has no cure but symptoms can be treated with topical corticosteroids, such as hydrocortisone and vitamin D. Avoiding the trigger allergen would prevent the occurrence of the eczema, as it would with contact dermatitis. Anti-inch creams help with the symptoms until the rash disappears on its own.
 It may be wise to see if trying different soaps and cleaning products prevent the contact rash.
It may be wise to see if trying different soaps and cleaning products prevent the contact rash.
Scalp psoriasis is treated with corticosteroid creams, phototherapy, and moisturizers for the symptoms. No cure has been found yet for psoriasis.
As a rule, the anti-fungal medicine, ketoconazole, is not used to treat skin infections; however, it has been effective for seborrheic dermatitis. The use of tea tree oil is also good to treat rashes as it is a natural antimicrobial. It can also be used for fungal or bacterial infections.
Turmeric is a very useful natural product for treating rash symptoms like redness, as well as to help stop the spreading. It’s anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial components have been very successful to treat rash behind the ear.
While some of these remedies may help to treat some of the symptoms, it’s important to know when to seek medical attention. It’s time to see the doctor or your dermatologist if the rash begins to spread or becomes worse.
A rash behind ear can sometimes go unnoticed unless it develops into an itchy or painful rash. It’s important to always maintain good hygiene by keeping the area clean and dry to prevent a rash from forming. Certain skin conditions that are unexplainable and unpreventable, however, must be attended to. Check the folds of your skin frequently and learn the cause of the rash before trying to treat it.
Related:
- Why Do I Have a Lump Behind My Ear?
- Rash on Stomach: Causes and Natural Treatments
- Lupus Rash: Signs, Symptoms and Treatments
- Rash around the Eyes: Causes and Natural Treatments
- Ear Infection in Babies: Causes, Treatments, and Prevention
